The signs of authoritarian and extremist assaults on the US constitutional democracy are ominous and increasing. The former president's explicit lawlessness and alignment with white supremacism; the governor of Florida's unrelenting assault on freedom of speech, academic freedom, the freedom of students to learn about their history, and even the freedom of major companies like Disney to express values of diversity and inclusion in their business activities; the evidence of conspiracy to commit acts of violent insurrection emerging from the trial of leaders of the Proud Boys (link) -- these are all developments that feel like the tremors that precede a volcano. Far right extremists are pressing their agenda, from paramilitary groups to high elected officials.
So where does the US public stand? What are the current attitudes of the citizens of our democracy? Researchers at the Allegheny College Center for Political Participation have disturbing news on that front as well, based on a national representative survey conducted in 2018 (link). Andrew Bloeser, Tarah Williams, Candaisy Crawford, and Brian Harward report the results of public opinion research on attitudes toward several related topics relating to disaffection from democratic norms. They published their primary results in "Are Stealth Democrats Really Committed to Democracy? Process Preferences Revisited" (link). They describe stealth democrats in these terms: "When it comes to governance, many Americans prefer uncompromising political leaders who take decisive action, rather than those who debate issues and are open to finding common ground" (1). Here is the abstract to the paper:
Scholarship on “stealth democracy” finds that many citizens want to avoid the debate and conflict that often come with democratic governance. This scholarship has argued that citizens adopt this posture because they are uncomfortable with disagreement and desire a more expedient political process that enables leaders to make decisions without discussion or compromise. We revisit this argument in light of recent political developments that suggest another reason why citizens may desire a more expedient political process. We examine the possibility that some citizens are not merely uncomfortable with disagreement but also want leaders who will aggressively protect them and champion their interests. Using a nationally representative survey, we ask citizens about their preferences for stealth democracy. We also ask questions that tap into their willingness to support leaders who would “bend the rules for supporters” and take aggressive action against political opponents. We find that a substantial component of the electorate continues to prefer a stealth version of democracy. However, we also find that many “stealth democrats” are willing to support leadership practices that would threaten or even undermine democratic norms. We argue that this evidence indicates that, in recent years, many citizens who appear to desire “stealth democracy” pose a threat to democracy itself.
In a more recent article in The Conversation (link) these researchers use the same data set to suggest that a disturbing fraction of the US population favor measures clearly associated with authoritarian rule. Consider responses to the statement, "The only way our country can solve its current problems is by supporting tough leaders who will crack down on those who undermine American values." 92% of "Strong Republicans" agree with this statement; 62% of Independents agree with the statement; and 59% of Strong Democrats in the sample agree with the statement. Consider another key statement: "To protect the interests of people like you, political leaders must sometimes bend the rules to get things done." 49% of Strong Republicans agree; 28% of Independents agree; and 36% of Strong Democrats agree. And what does this statement involve? It involves the rule of law.
These findings suggest a significant erosion of support for constitutional democracy in favor of strongman government like that of Viktor Orbán in Hungary.
Why would US citizens develop a set of political values that favor the restriction or elimination of limits on the use of executive power -- by governors or presidents -- that very well could lead to harm to themselves and their families? A constitution exists to ensure equal treatment to all citizens and to establish equal liberties for all citizens; so why would some citizens favor authoritarian rule over constitutional protections? One possible motivation is the misplaced confidence that the strongman who emerges will naturally protect the interests of one's own group. But logic and history both suggest that all citizens benefit from constitutional and legal protections, and surrendering those for shortterm anxieties is a horrible mistake.
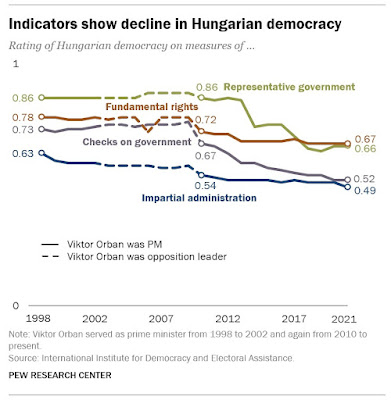
Seeing the behavior of the preponderance of GOP elected officials and the opinion research data offered by the Allegheny group raises major concerns about the future of US democracy -- as Levitsky and Ziblatt argued in How Democracies Die. Similar processes have already advanced even further in other countries, including Hungary and India. Compare the 2018 Allegheny College survey of US voters with a survey of Hungarian voters conducted by the Pew Research Center in 2022 (link). The Pew survey of Hungarian voters suggests a decline in Hungarian democracy under Orbán's rule since about 2012. (Similar results show up in a 2017 public opinion survey conducted in Hungary by the Center for Insights in Survey Research; link.)What will it take to reinvigorate broad public allegiance to the institutions of a constitutional democracy? We would like to imagine that reactionary developments like overturning Roe v. Wade would have the effect of mobilizing vast numbers of voters in support of the rule of law and the voice of the people, and indeed the 2022 elections showed that effect (link). But how will a weary public and "stealth democrats" deal with continuing efforts to restrict voting rights, create gerrymandered districts, and assault basic constitutional rights like freedom of speech and learning in public schools? Will we gain the commitment and courage to speak and act in support of our democracy?
And what will it take to struggle against the anti-democratic efforts of politicians like Kari Lake in Arizona? (The very idea, now the subject of speculation in Arizona, that Lake might be a strong contender in the 2024 Senate race in Arizona is almost beyond belief. What voter could ever support a person running for elected office who has already demonstrated that she will only accept the outcome of the election if it goes in her favor?) When will the reputation for rejecting the laws and norms of a democracy become a political liability for these unscrupulous politicians?



This is disturbing. It reveals a different twist on the old notion of a 'silent majority'. If more people find distaste in disagreement;want to remove the impediments of debate, we are in a heap of trouble. Iron-fisted Fascism made a living off silence and fear. Leaders of the totalitarian stripe may not appear so ruthless, but their endgame is the same: absolute power. Rhetorical question: is this part and parcel of current attacks on academic freedom, and a quasi-persecution of philosophy? Those who pay attention know philosophy loves a good argument. I suppose that is why silent folks, leaning towards more conservative democracy (or none at all) find free discourse problematic? I am working on some notes on custom and tradition. Will hold those, for now.
ReplyDelete